This is the first of three case studies that are used to guide the reader through the six steps outlined in Six-Step Relational Database Design™. The most important outputs of the six step database design process are depicted here, but the details of each of the steps and intermediary outputs are detailed in the book.
| What's on this page |
|---|
| Scenario List of entities and their corresponding attributes Entity-Relationship diagrams Relational-Model diagram SQL commands |
Scenario
A corporate office intends to implement a digital front desk solution to assist receptionists in managing key administrative functions for senior management staff (e.g. executives, department heads). The application for the new system will streamline the management of appointments, meeting rooms, visitors, and administrative tasks.
The application must be capable of:
- Tracking all appointments scheduled for senior management staff.
- Managing meeting rooms assigned to these appointments and preventing scheduling conflicts.
- Recording details of visitors attending appointments, including check-in/check-out times (visitor log).
- Managing administrative tasks associated with senior staff and linking them to relevant appointments and visitors, where applicable.
Additionally, the system must be password-protected and support role-based access control, ensuring that users (e.g. receptionists, assistants, senior staff) can only access features appropriate to their roles. User login activity must also be recorded.
To promote transparency and accountability, the application should include basic auditing features, such as tracking who created or modified records and when. Extensive logging of database changes is not required.
Your job is to design a database that will serve as the back end of this application.
List of entities and their corresponding attributes
Below is the list of entities and their corresponding attributes that is output from Step 1 of the six step database design process as described in the Six-Step Relational Database Design™ book:
| SeniorStaff |
|---|
| (PK) StaffId |
| LastName |
| FirstName |
| MI |
| Title |
| Department |
| Extension |
| Mobile |
| Status |
| CreatedBy |
| CreatedOn |
| LastUpdatedBy |
| LastUpdatedOn |
| IsDeleted |
| DeletedBy |
| DeletedOn |
| Appointments |
|---|
| (PK) AppointmentId |
| AppointmentDate |
| StartTime |
| EndTime |
| Purpose |
| Status |
| Comments |
| CreatedBy |
| CreatedOn |
| LastUpdatedBy |
| LastUpdatedOn |
| IsDeleted |
| DeletedBy |
| DeletedOn |
| MeetingRooms |
|---|
| (PK) RoomId |
| RoomName |
| RoomNumber |
| Location |
| Capacity |
| Status |
| CreatedBy |
| CreatedOn |
| LastUpdatedBy |
| LastUpdatedOn |
| IsDeleted |
| DeletedBy |
| DeletedOn |
| Visitors |
|---|
| (PK) VisitorId |
| LastName |
| FirstName |
| Mobile |
| Organization |
| PurposeOfVisit |
| CreatedBy |
| CreatedOn |
| LastUpdatedBy |
| LastUpdatedOn |
| IsDeleted |
| DeletedBy |
| DeletedOn |
| VisitationLog |
|---|
| (PK) VisitationLogId |
| BadgeNumber |
| CheckInDate |
| CheckInTime |
| CheckOutTime |
| CreatedBy |
| CreatedOn |
| LastUpdatedBy |
| LastUpdatedOn |
| IsDeleted |
| DeletedBy |
| DeletedOn |
| AdministrativeTasks |
|---|
| (PK) TaskId |
| TaskName |
| TaskDescription |
| TaskPriority |
| Deadline |
| Status |
| CreatedBy |
| CreatedOn |
| LastUpdatedBy |
| LastUpdatedOn |
| IsDeleted |
| DeletedBy |
| DeletedOn |
| Users |
|---|
| (PK) UserId |
| Login |
| UserName |
| PasswordHash |
| PasswordSalt |
| IsActive |
| CreatedBy |
| CreatedOn |
| LastUpdatedBy |
| LastUpdatedOn |
| IsDeleted |
| DeletedBy |
| DeletedOn |
| Roles |
|---|
| (PK) RoleId |
| RoleName |
| RoleDescription |
| Comments |
| CreatedBy |
| CreatedOn |
| LastUpdatedBy |
| LastUpdatedOn |
| IsDeleted |
| DeletedBy |
| DeletedOn |
| LoginEntries |
|---|
| (PK) LoginEntryId |
| LoggedOn |
| LoggedOff |
| IPAddress |
| CreatedOn |
| ModifiedOn |
Top
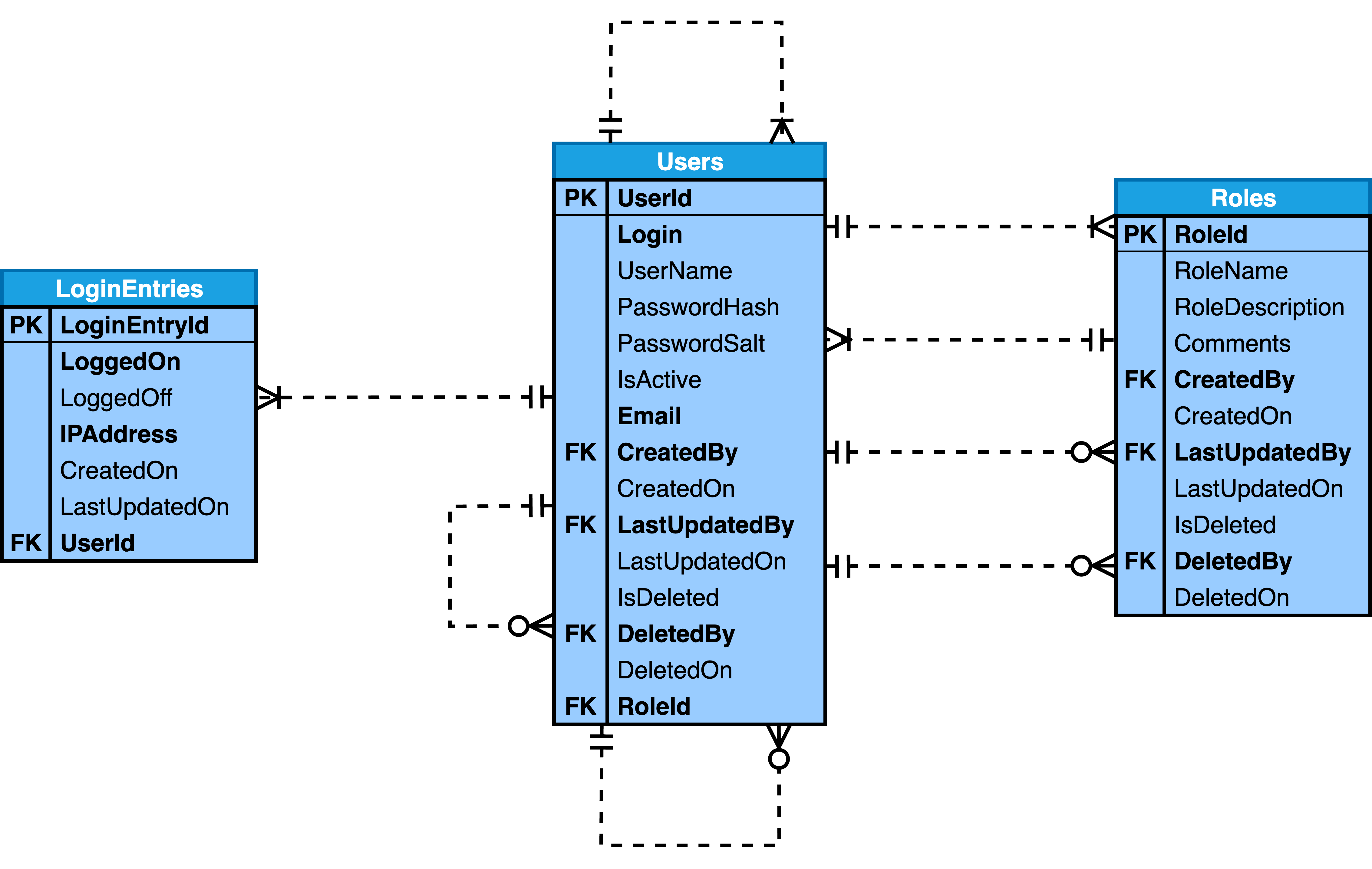
Entity-Relationship diagrams
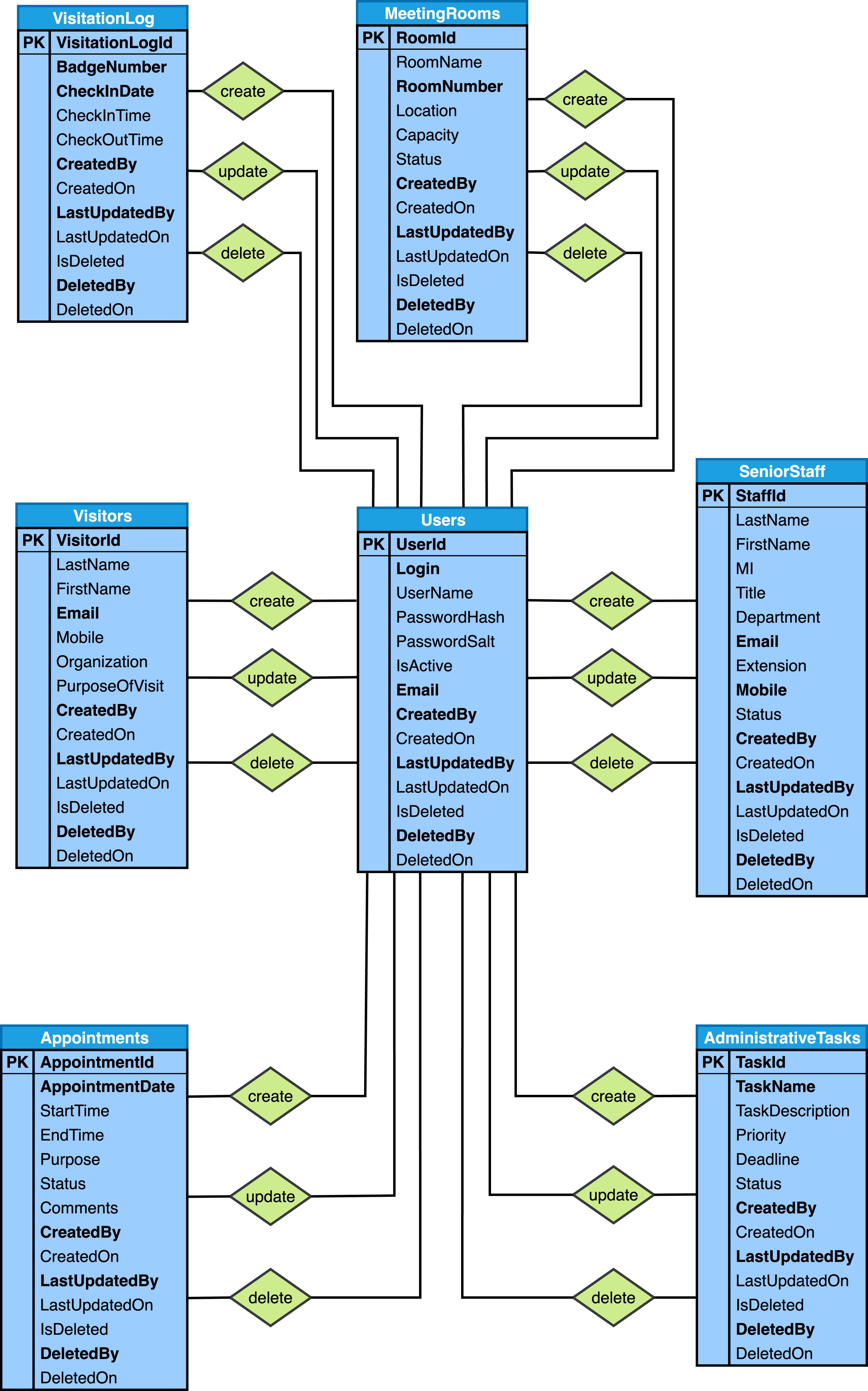
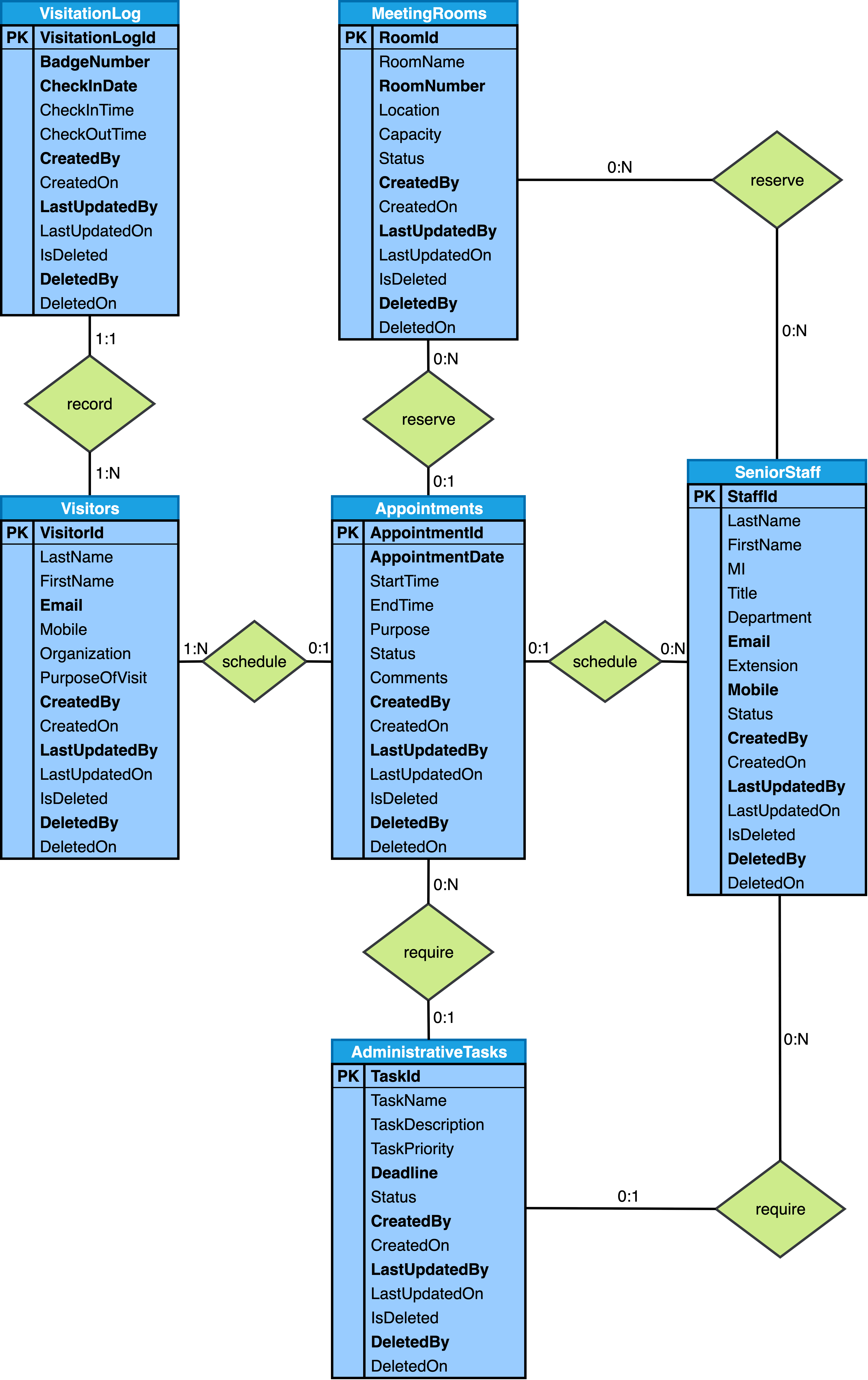
Below are the Simplified Entity-Relationship diagrams that are output from Step 3 of the six step database design process as described in the Six-Step Relational Database Design™ book:
Below are the Detailed Entity-Relationship diagrams that are output from Step 5 of the six step database design process as described in the Six-Step Relational Database Design™ book:
Top
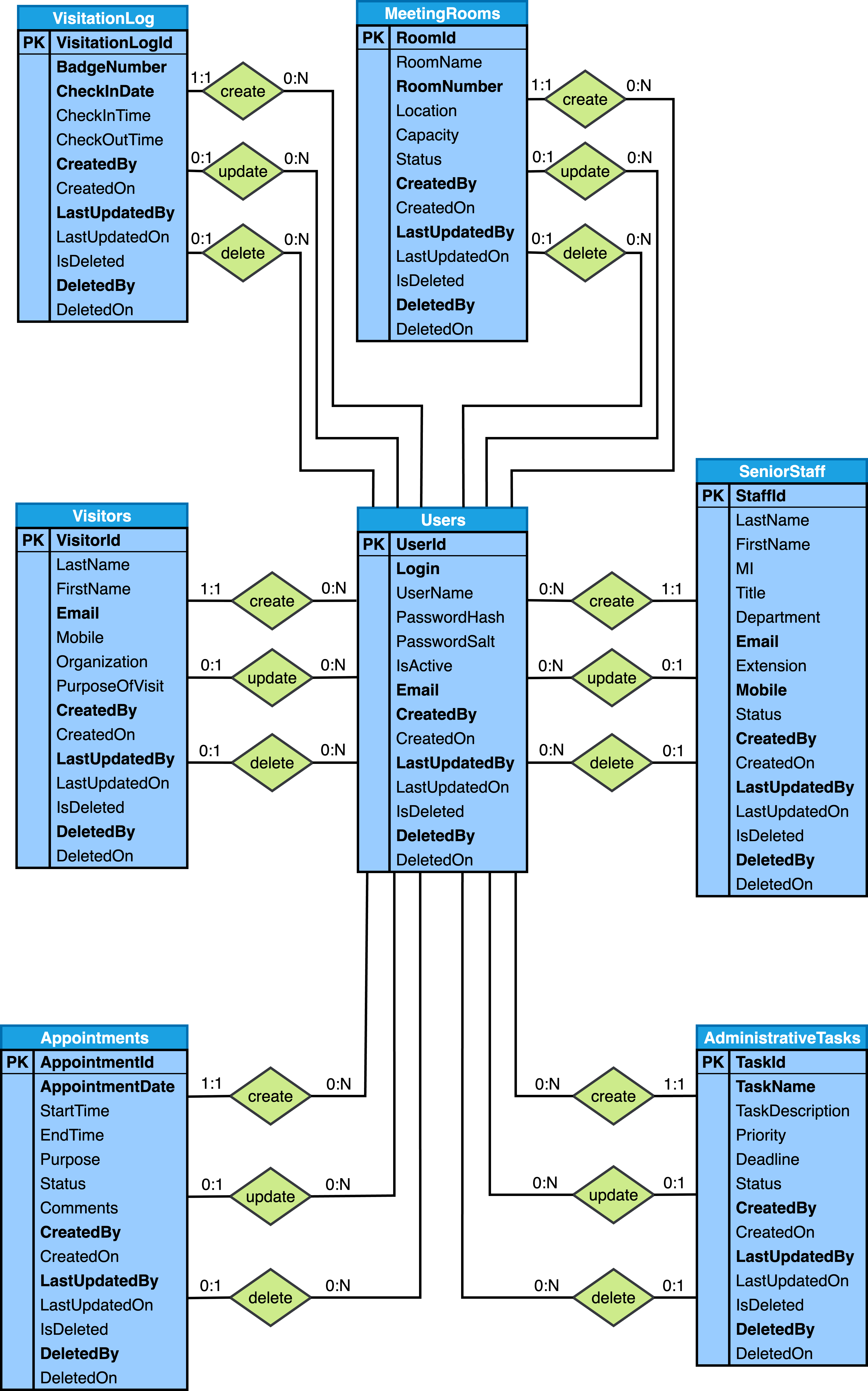
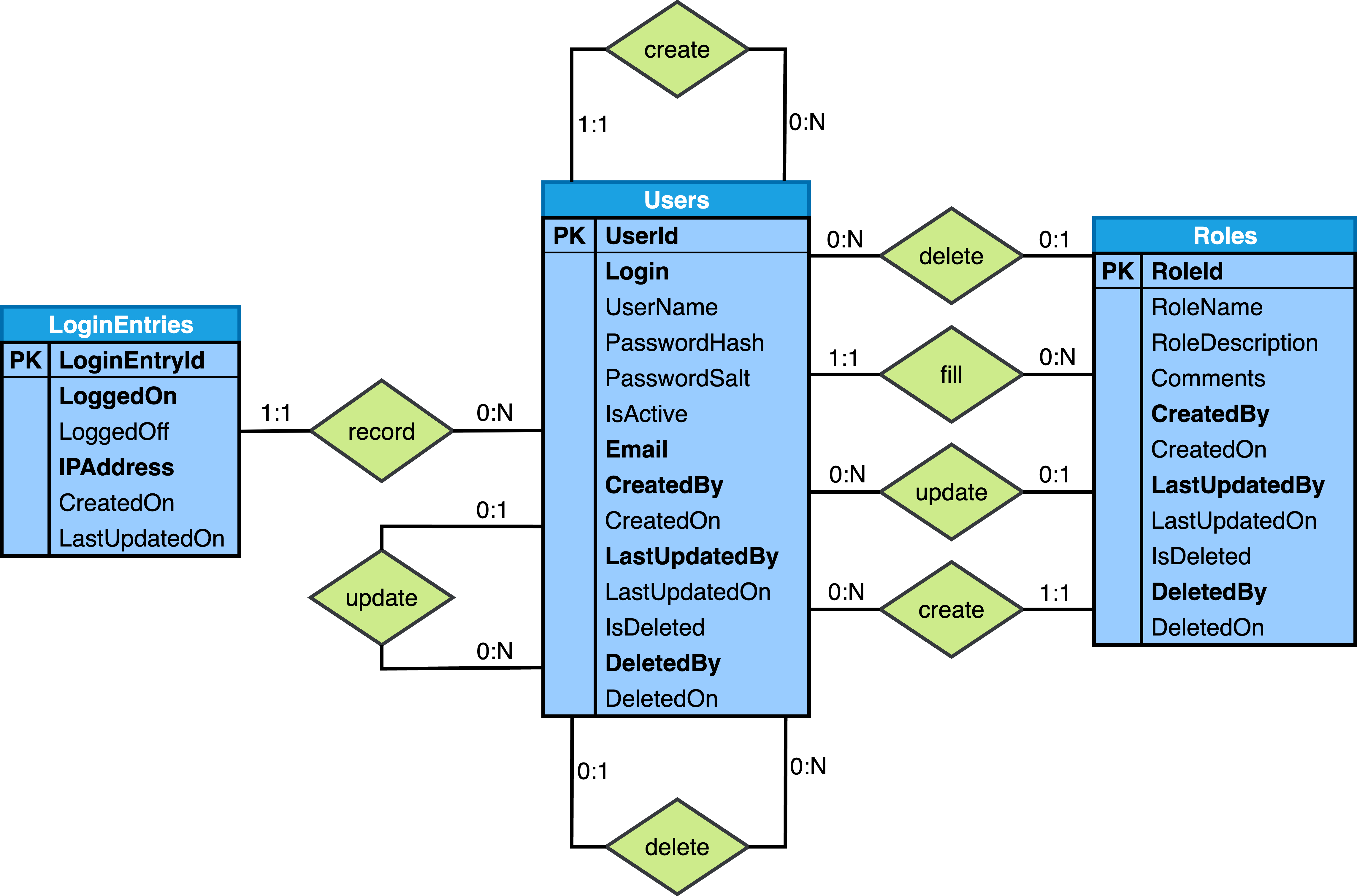
Relational-Model diagram
Below are the Relational-Model diagrams that are output from Step 6 of the six step database design process as described in theSix-Step Relational Database Design™ book:
Top
SQL commands
The SQL commands below can be used to implement the design depicted above in a MySQL database. Some modifications will be necessary to execute these commands on MS SQL Server, Oracle, or any other RDBMS. Detailed implementation considerations can be found in the Six-Step Relational Database Design™ book.
CREATE TABLE Users ( UserId SERIAL, Login VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL, UserName VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL, PasswordHash VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL, PasswordSalt VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL, IsActive BOOLEAN DEFAULT '1', Role VARCHAR(25) NOT NULL, Email VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL, CreatedBy BIGINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL, CreatedOn DATETIME DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP, LastUpdatedBy BIGINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL, LastUpdatedOn DATETIME DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP, IsDeleted BOOLEAN DEFAULT '0', DeletedBy BIGINT UNSIGNED NULL, DeletedOn DATETIME NULL, PRIMARY KEY (UserId), FOREIGN KEY CreatedBy (CreatedBy) REFERENCES Users (UserId) ON UPDATE CASCADE ON DELETE RESTRICT, FOREIGN KEY LastUpdatedBy (LastUpdatedBy) REFERENCES Users (UserId) ON UPDATE CASCADE ON DELETE RESTRICT, FOREIGN KEY DeletedBy (DeletedBy) REFERENCES Users (UserId) ON UPDATE CASCADE ON DELETE RESTRICT, UNIQUE INDEX Login (Login), UNIQUE INDEX Email (Email) ); CREATE TABLE LoginEntries ( LogEntryId SERIAL, LoggedOn DATETIME DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP, LoggedOff DATETIME DEFAULT NULL, IPAddress VARCHAR(46) NOT NULL, CreatedOn DATETIME DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP, LastUpdatedOn DATETIME DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP, UserId BIGINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (LogEntryId), FOREIGN KEY UserId (UserId) REFERENCES Users (UserId) ON UPDATE CASCADE ON DELETE RESTRICT, INDEX LoggedOn (LoggedOn) ); CREATE TABLE Visitors ( VisitorId SERIAL, LastName VARCHAR(35) NOT NULL, FirstName VARCHAR(35) NOT NULL, Email VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL, Mobile VARCHAR(14) DEFAULT NULL, Organization VARCHAR(150) DEFAULT NULL, PurposeOfVisit VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL, CreatedBy BIGINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL, CreatedOn DATETIME DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP, LastUpdatedBy BIGINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL, LastUpdatedOn DATETIME DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP, IsDeleted BOOLEAN DEFAULT '0', DeletedBy BIGINT UNSIGNED NULL, DeletedOn DATETIME NULL, PRIMARY KEY (VisitorId), INDEX FullName (LastName, FirstName), UNIQUE INDEX Email (Email), INDEX Mobile (Mobile), FOREIGN KEY CreatedBy (CreatedBy) REFERENCES Users (UserId) ON UPDATE CASCADE ON DELETE RESTRICT, FOREIGN KEY LastUpdatedBy (LastUpdatedBy) REFERENCES Users (UserId) ON UPDATE CASCADE ON DELETE RESTRICT, FOREIGN KEY DeletedBy (DeletedBy) REFERENCES Users (UserId) ON UPDATE CASCADE ON DELETE RESTRICT ); CREATE TABLE MeetingRooms ( RoomId SERIAL, RoomName VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL, RoomNumber VARCHAR(35) NOT NULL, Location VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL, Capacity SMALLINT DEFAULT 1, Status VARCHAR(20) DEFAULT 'Available', CreatedBy BIGINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL, CreatedOn DATETIME DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP, LastUpdatedBy BIGINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL, LastUpdatedOn DATETIME DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP, IsDeleted BOOLEAN DEFAULT '0', DeletedBy BIGINT UNSIGNED NULL, DeletedOn DATETIME NULL, PRIMARY KEY (RoomId), UNIQUE INDEX RoomNumber (RoomNumber), FOREIGN KEY CreatedBy (CreatedBy) REFERENCES Users (UserId) ON UPDATE CASCADE ON DELETE RESTRICT, FOREIGN KEY LastUpdatedBy (LastUpdatedBy) REFERENCES Users (UserId) ON UPDATE CASCADE ON DELETE RESTRICT, FOREIGN KEY DeletedBy (DeletedBy) REFERENCES Users (UserId) ON UPDATE CASCADE ON DELETE RESTRICT ); CREATE TABLE SeniorStaff ( StaffId SERIAL, LastName VARCHAR(35) NOT NULL, FirstName VARCHAR(35) NOT NULL, MI VARCHAR(5) DEFAULT NULL, Title VARCHAR(10) DEFAULT NULL, Department VARCHAR(35) NOT NULL, Email VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL, Extension VARCHAR(7) DEFAULT NULL, Mobile VARCHAR(14) DEFAULT NULL, Status VARCHAR(20) DEFAULT 'Full Time', CreatedBy BIGINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL, CreatedOn DATETIME DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP, LastUpdatedBy BIGINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL, LastUpdatedOn DATETIME DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP, IsDeleted BOOLEAN DEFAULT '0', DeletedBy BIGINT UNSIGNED NULL, DeletedOn DATETIME NULL, PRIMARY KEY (StaffId), INDEX FullName (LastName, FirstName), UNIQUE INDEX Email (Email), INDEX Mobile (Mobile), FOREIGN KEY CreatedBy (CreatedBy) REFERENCES Users (UserId) ON UPDATE CASCADE ON DELETE RESTRICT, FOREIGN KEY LastUpdatedBy (LastUpdatedBy) REFERENCES Users (UserId) ON UPDATE CASCADE ON DELETE RESTRICT, FOREIGN KEY DeletedBy (DeletedBy) REFERENCES Users (UserId) ON UPDATE CASCADE ON DELETE RESTRICT ); CREATE TABLE VisitationLog ( VisitationLogId SERIAL, BadgeNumber VARCHAR(10) NOT NULL, CheckInDate DATE NOT NULL, CheckInTime TIME NOT NULL, CheckOutTime TIME DEFAULT NULL, VisitorId BIGINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL, CreatedBy BIGINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL, CreatedOn DATETIME DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP, LastUpdatedBy BIGINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL, LastUpdatedOn DATETIME DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP, IsDeleted BOOLEAN DEFAULT '0', DeletedBy BIGINT UNSIGNED NULL, DeletedOn DATETIME NULL, PRIMARY KEY (VisitationLogId), INDEX CheckinDate (CheckinDate), FOREIGN KEY CreatedBy (CreatedBy) REFERENCES Users (UserId) ON UPDATE CASCADE ON DELETE RESTRICT, FOREIGN KEY LastUpdatedBy (LastUpdatedBy) REFERENCES Users (UserId) ON UPDATE CASCADE ON DELETE RESTRICT, FOREIGN KEY DeletedBy (DeletedBy) REFERENCES Users (UserId) ON UPDATE CASCADE ON DELETE RESTRICT, FOREIGN KEY VisitorId (VisitorId) REFERENCES Visitors (VisitorId) ON UPDATE CASCADE ON DELETE RESTRICT ); CREATE TABLE Appointments ( AppointmentId SERIAL, AppointmentDate DATE NOT NULL, StartTime TIME NOT NULL, EndTime TIME NOT NULL, Purpose VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL, Status VARCHAR(20) DEFAULT 'Unconfirmed', Comments VARCHAR(1000) DEFAULT NULL, RoomId BIGINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL, VisitorId BIGINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL, StaffId BIGINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL, CreatedBy BIGINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL, CreatedOn DATETIME DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP, LastUpdatedBy BIGINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL, LastUpdatedOn DATETIME DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP, IsDeleted BOOLEAN DEFAULT '0', DeletedBy BIGINT UNSIGNED NULL, DeletedOn DATETIME NULL, PRIMARY KEY (AppointmentId), INDEX AppointmentDate (AppointmentDate), FOREIGN KEY CreatedBy (CreatedBy) REFERENCES Users (UserId) ON UPDATE CASCADE ON DELETE RESTRICT, FOREIGN KEY LastUpdatedBy (LastUpdatedBy) REFERENCES Users (UserId) ON UPDATE CASCADE ON DELETE RESTRICT, FOREIGN KEY DeletedBy (DeletedBy) REFERENCES Users (UserId) ON UPDATE CASCADE ON DELETE RESTRICT, FOREIGN KEY RoomId (RoomId) REFERENCES MeetingRooms (RoomId) ON UPDATE CASCADE ON DELETE RESTRICT, FOREIGN KEY VisitorId (VisitorId) REFERENCES Visitors (VisitorId) ON UPDATE CASCADE ON DELETE RESTRICT, FOREIGN KEY StaffId (StaffId) REFERENCES SeniorStaff (StaffId) ON UPDATE CASCADE ON DELETE RESTRICT ); CREATE TABLE AdministrativeTasks ( TaskId SERIAL, TaskName VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL, TaskDescription VARCHAR(1000) NOT NULL, TaskPriority VARCHAR(20) DEFAULT 'Normal', Deadline DATETIME DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP, Status VARCHAR(20) DEFAULT 'Not Started', AppointmentId BIGINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL, StaffId BIGINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL, CreatedBy BIGINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL, CreatedOn DATETIME DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP, LastUpdatedBy BIGINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL, LastUpdatedOn DATETIME DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP, IsDeleted BOOLEAN DEFAULT '0', DeletedBy BIGINT UNSIGNED NULL, DeletedOn DATETIME NULL, PRIMARY KEY (TaskId), FOREIGN KEY CreatedBy (CreatedBy) REFERENCES Users (UserId) ON UPDATE CASCADE ON DELETE RESTRICT, FOREIGN KEY LastUpdatedBy (LastUpdatedBy) REFERENCES Users (UserId) ON UPDATE CASCADE ON DELETE RESTRICT, FOREIGN KEY DeletedBy (DeletedBy) REFERENCES Users (UserId) ON UPDATE CASCADE ON DELETE RESTRICT, FOREIGN KEY AppointmentId (AppointmentId) REFERENCES Appointments (AppointmentId) ON UPDATE CASCADE ON DELETE RESTRICT, FOREIGN KEY StaffId (StaffId) REFERENCES SeniorStaff (StaffId) ON UPDATE CASCADE ON DELETE RESTRICT ); CREATE TABLE SeniorStaffMeetingRooms ( StaffRoomId SERIAL, MeetingDate DATE NOT NULL, StartTime TIME NOT NULL, EndTime TIME NOT NULL, Purpose VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL, StaffId BIGINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL, RoomId BIGINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL, CreatedBy BIGINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL, CreatedOn DATETIME DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP, LastUpdatedBy BIGINT UNSIGNED NOT NULL, LastUpdatedOn DATETIME DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP, IsDeleted BOOLEAN DEFAULT '0', DeletedBy BIGINT UNSIGNED NULL, DeletedOn DATETIME NULL, PRIMARY KEY (StaffRoomId), INDEX MeetingDate (MeetingDate), FOREIGN KEY CreatedBy (CreatedBy) REFERENCES Users (UserId) ON UPDATE CASCADE ON DELETE RESTRICT, FOREIGN KEY LastUpdatedBy (LastUpdatedBy) REFERENCES Users (UserId) ON UPDATE CASCADE ON DELETE RESTRICT, FOREIGN KEY DeletedBy (DeletedBy) REFERENCES Users (UserId) ON UPDATE CASCADE ON DELETE RESTRICT, FOREIGN KEY StaffId (StaffId) REFERENCES SeniorStaff (StaffId) ON UPDATE CASCADE ON DELETE RESTRICT, FOREIGN KEY RoomId (RoomId) REFERENCES MeetingRooms (RoomId) ON UPDATE CASCADE ON DELETE RESTRICT );
| Other Case Studies |
|---|
| Case Study 2 Case Study 3 |





Follow