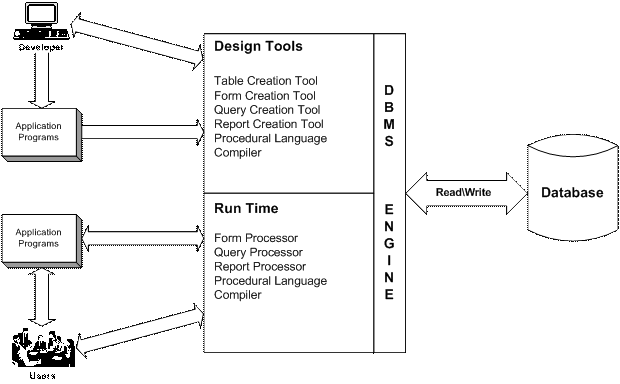
There are three main components of a database management system (from David M Kroenke):
- Design Tools Subsystem – This contains a set of tools to facilitate the design and creation of the database and its applications. It typically includes tools for creating tables, forms queries and reports.
- Run-Time Subsystem – This subsystem is responsible for processing the application components that have been developed using the design tools.
- DBMS Engine – This takes commands from the run-time subsystem, the design tools subsystem, or directly from the application and then translates them into commands to read from or write to the actual physical file.
- Database –This is the physical file that contains the actual data that is accessed and manipulated by the DBMS via the DBMS Engine.
Database Models
A database model is a collection of logical constructs used to represent the data structure and the data relationships found within the database. Basically, database models may be grouped into two categories: conceptual models and implementation models (physical models). The conceptual model is concerned with what is represented in the database rather than how it is represented, and the implementation or physical model is concerned with how the data is going to be represented in the database.
As discussed previously, in databases relationships exist between the data that is in the database; Conceptual models capture this relationship.

Follow