A subnet is a physical segment of a TCP/IP network that uses IP addresses derived from a single Network ID. Large networks are typically divided into several subnets for ease of management and sometimes because of physical limitations. Each segment of the network, or subnet, would use a different Network ID or Subnet ID.
Subnet Masks
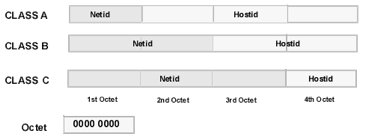
As mentioned before, an IP address is made up of two parts: the Network ID and the Host ID, and that there are three classes of IP addresses: Class A, Class B and Class C. IP addressing uses a subnet mask to determine what part of he IP address is the Network ID and what part is the Host ID.
In a subnet mask, a 1 is used to mask out the network portion of an IP address. The subnet mask is ANDed together with the IP address to produce only the Network ID; the remaining part is the Host ID. Each of the three address classes has what is called a default subnet mask that uses the decimal number 255 for each octet (8 bits) in the address that corresponds to the network portion of the IP address. (The number 255 is 11111111 in binary, which fills all 8 bit positions in an IP address octet.) Thus, the default Class A subnet mask is 255.0.0.0, the default Class B subnet mask is 255.255.0.0, and the default Class C subnet mask is 255.255.255.0. (Tomsho, Tittel, Johnson, pg. 202)
Subnets
As discussed previously, a subnet is a physical segment of a TCP/IP network that uses IP addresses derived from a single Network ID. Network and Host IDs vary as follows:
The Subnet ID is derived from breaking up the Host ID:
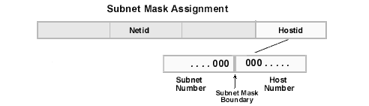
An example of this would be:

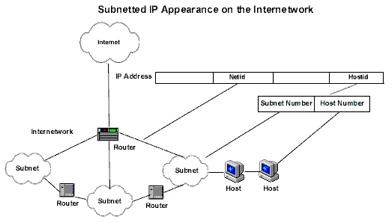
Hence, a subnetted network will thus look like:
IP Configuration
If a network is divided into subnets, then each subnet must have a router (default gateway) that links it to other parts of the network (subnets). The router allows computing devices in one segment of the network (subnet) to be able to access devices outside that segment – the router then acts as a gateway to the rest of the network.
Every network with subnets must have as part of its IP configuration:
- Its IP address,
- Its subnet mask, and
- Its default gateway – the default gateway being the address of the router.

Follow